Model Fine-tuning Process
Complete Guide to Qwen3-4B Model Fine-tuning
This document provides a comprehensive guide to fine-tuning the Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 model, covering everything from environment setup to model deployment in a one-stop guide.
First, Start the Notebook Service
Follow the interface operations below to start Jupyter Notebook:
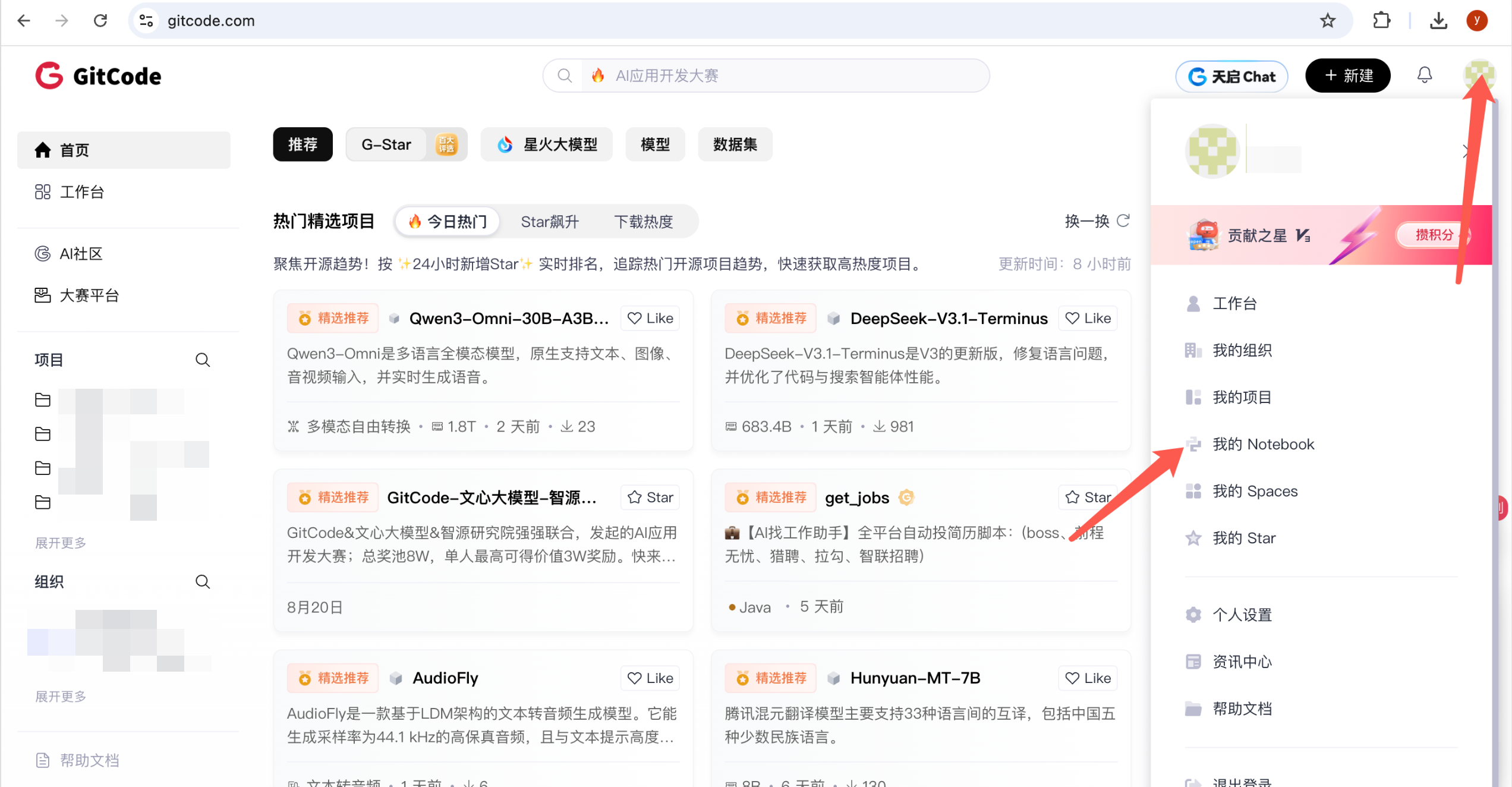
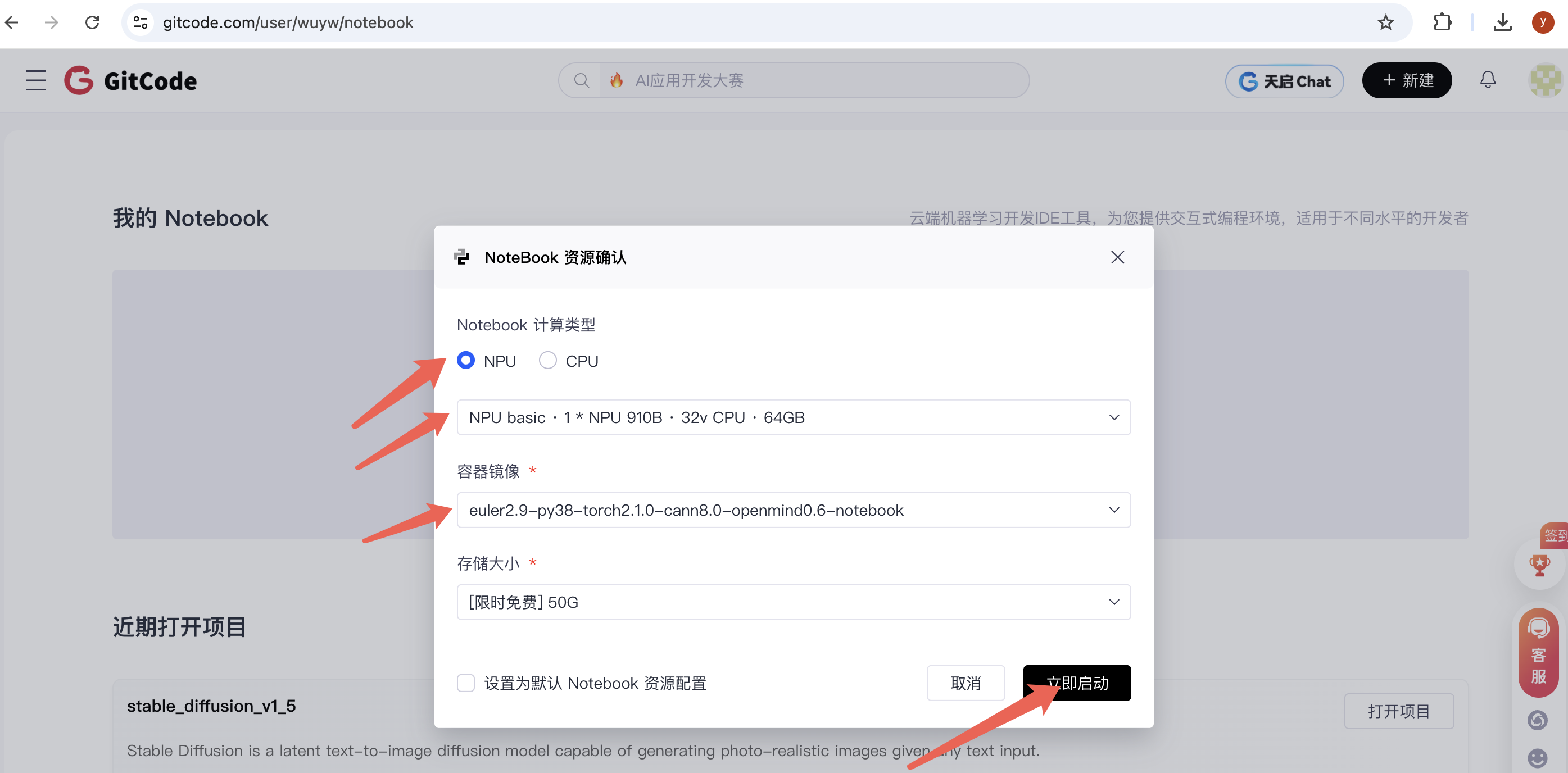
Table of Contents
- Environment Installation
- Model Download
- Dataset Preparation
- Model Fine-tuning
- Performance Evaluation
- Model Deployment
1. Environment Installation
1.1 Install Miniconda
Windows System:
- Visit Miniconda Official Website to download the installer
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to complete installation
- Restart the command prompt
macOS/Linux Systems:
# macOS
brew install miniconda
# Linux
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
source ~/.bashrc
1.2 Create Python Environment
# Create and activate environment
conda create -n myenv python=3.10
conda activate myenv
# Verify installation
python --version
1.3 Configure Jupyter Notebook
# Install Jupyter
pip install jupyter ipykernel ipywidgets
# Register kernel
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=myenv --display-name="Python (myenv)"
# Start Notebook
jupyter notebook
Important Note: Select the Python (myenv) kernel in the Notebook
1.4 Install Dependencies
Run in the activated myenv environment:
# One-click installation of all dependencies
pip install datasets==2.21.0 addict swanlab accelerate transformers numpy==1.24.4 scipy openmind-hub modelscope torch pandas torch_npu==2.5.1
1.5 Environment Verification
Run in the first cell of Jupyter Notebook:
import sys
import os
# Configure environment variables
os.environ["OPENMIND_HUB_ENDPOINT"] = "https://hub.gitcode.com"
# Verify main packages
packages = ['torch', 'transformers', 'datasets', 'swanlab', 'openmind_hub']
for pkg in packages:
try:
module = __import__(pkg)
print(f"✓ {pkg}: {getattr(module, '__version__', 'installed')}")
except ImportError:
print(f"✗ {pkg}: not installed")
2. Model Download
2.1 Download Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507
from openmind_hub import snapshot_download
import os
# Set environment variables
os.environ["OPENMIND_HUB_ENDPOINT"] = "https://hub.gitcode.com"
# Download model (note path format)
snapshot_download(
"hf_mirrors%2FQwen/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507",
local_dir='./model/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507'
)
After download completion, the model will be saved in the ./model/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507/ directory.
3. Dataset Preparation
3.1 Load and Process Data
from modelscope.msdatasets import MsDataset
import json
import random
# Set random seed
random.seed(42)
# Load medical dataset
ds = MsDataset.load('krisfu/delicate_medical_r1_data', subset_name='default', split='train')
data_list = list(ds)
# Data split (9:1)
random.shuffle(data_list)
split_idx = int(len(data_list) * 0.9)
train_data = data_list[:split_idx]
val_data = data_list[split_idx:]
# Save data
for data, filename in [(train_data, 'train.jsonl'), (val_data, 'val.jsonl')]:
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for item in data:
json.dump(item, f, ensure_ascii=False)
f.write('\n')
print(f"Training set: {len(train_data)} items, Validation set: {len(val_data)} items")
4. Model Fine-tuning
4.1 SwanLab Configuration
SwanLab is used for monitoring the training process:
- Visit SwanLab Official Website to register and get API Key
- Login in the Notebook:
import swanlab
swanlab.login(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY", save=True)
4.2 Prepare Training Code
import json
import pandas as pd
import torch
import torch_npu
from datasets import Dataset
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, TrainingArguments, Trainer, DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
import os
# Project configuration
os.environ["SWANLAB_PROJECT"] = "qwen3-sft-medical"
PROMPT = "You are a medical expert, you need to provide thoughtful answers based on user questions."
MAX_LENGTH = 2048
# Data conversion function
def dataset_jsonl_transfer(origin_path, new_path):
messages = []
with open(origin_path, "r") as file:
for line in file:
data = json.loads(line)
output = f"<think>{data['think']}</think> \n {data['answer']}"
message = {
"instruction": PROMPT,
"input": data["question"],
"output": output,
}
messages.append(message)
with open(new_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
for message in messages:
file.write(json.dumps(message, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
# Preprocessing function
def process_func(example):
instruction = tokenizer(
f"<|im_start|>system\n{PROMPT}<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n{example['input']}<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n",
add_special_tokens=False,
)
response = tokenizer(f"{example['output']}", add_special_tokens=False)
input_ids = instruction["input_ids"] + response["input_ids"] + [tokenizer.pad_token_id]
attention_mask = instruction["attention_mask"] + response["attention_mask"] + [1]
labels = [-100] * len(instruction["input_ids"]) + response["input_ids"] + [tokenizer.pad_token_id]
# Truncation handling
if len(input_ids) > MAX_LENGTH:
input_ids = input_ids[:MAX_LENGTH]
attention_mask = attention_mask[:MAX_LENGTH]
labels = labels[:MAX_LENGTH]
return {"input_ids": input_ids, "attention_mask": attention_mask, "labels": labels}
4.3 Load Model and Data
# Load model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
"./model/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507",
use_fast=False,
trust_remote_code=True
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"./model/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507",
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16
).to("npu:0")
model.enable_input_require_grads()
# Process dataset
dataset_jsonl_transfer("train.jsonl", "train_format.jsonl")
dataset_jsonl_transfer("val.jsonl", "val_format.jsonl")
# Create training data
train_df = pd.read_json("train_format.jsonl", lines=True)
train_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(train_df).map(process_func, remove_columns=train_df.columns)
eval_df = pd.read_json("val_format.jsonl", lines=True)
eval_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(eval_df).map(process_func, remove_columns=eval_df.columns)
4.4 Training Configuration and Start Training
# Training parameters
args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./output/Qwen3-4B",
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
per_device_eval_batch_size=1,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
eval_strategy="steps",
eval_steps=100,
logging_steps=10,
num_train_epochs=2,
save_steps=400,
learning_rate=1e-4,
save_on_each_node=True,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
report_to="swanlab",
run_name="qwen3-4B-medical",
)
# Create trainer
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
data_collator=DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(tokenizer=tokenizer, padding=True),
)
# Start training
trainer.train()
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1 Inference Testing
def predict(messages, model, tokenizer):
device = "npu:0"
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(device)
generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs.input_ids, max_new_tokens=MAX_LENGTH)
generated_ids = [output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)]
return tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
# Test samples
test_df = pd.read_json("val_format.jsonl", lines=True)[:3]
test_results = []
for _, row in test_df.iterrows():
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": row['instruction']},
{"role": "user", "content": row['input']}
]
response = predict(messages, model, tokenizer)
result = f"Question: {row['input']}\nAnswer: {response}\n{'='*50}"
test_results.append(swanlab.Text(result))
print(result)
# Log to SwanLab
swanlab.log({"Test Results": test_results})
swanlab.finish()
5.2 Evaluation Metrics
The fine-tuned model should possess the following capabilities:
- Understand medical professional questions
- Provide structured thinking process (
<think>tags) - Give accurate medical advice
- Maintain professional medical terminology
6. Model Deployment
6.1 Upload to AtomGit
Method 1: Using OpenMind Hub
from openmind_hub import push_to_hub
push_to_hub(
repo_id="your_username/qwen3-4b-medical-finetuned",
folder_path="./output/Qwen3-4B",
token="your_gitcode_token"
)
Method 2: Git Commands
cd ./output/Qwen3-4B
git init
git remote add origin https://gitcode.com/your_username/qwen3-4b-medical-finetuned.git
git add .
git commit -m "Add fine-tuned Qwen3-4B medical model"
git push -u origin main
6.2 Create Model Description
Create a README.md file to describe the model:
# Qwen3-4B Medical Fine-tuned Model
## Model Information
- **Base Model**: Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507
- **Training Data**: Medical Q&A dataset
- **Training Epochs**: 2 epochs
- **Learning Rate**: 1e-4
## Usage
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("your_username/qwen3-4b-medical-finetuned")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("your_username/qwen3-4b-medical-finetuned")
Summary
This guide covers the complete process of fine-tuning the Qwen3-4B medical model:
- Environment Setup → Conda environment + Jupyter configuration
- Model Preparation → Download pre-trained model
- Data Processing → Medical dataset preprocessing
- Model Training → Fine-tuning training configuration
- Performance Verification → Inference testing and evaluation
- Model Release → Upload to GitCode platform
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What to do if running out of memory during training?
A: Reduce per_device_train_batch_size or increase gradient_accumulation_steps
Q: How to choose different kernels?
A: In Jupyter, select Kernel → Change kernel → Python (myenv)
Q: What to do if SwanLab shows abnormalities? A: Check if the API Key is correct and network is normal
Q: How to optimize if model performance is unsatisfactory? A: Adjust learning rate, increase training epochs, optimize data quality
Need technical support? Please refer to detailed instructions in each section or contact the technical team.